HEMOSTASIS COAGULATION RESEARCH REAGENTS ENZYMES FACTOR VIIA
Human FVIIa
Structure: 2 subunits with N-terminal end derived from light chains (MW = 20 000), COOH end derived from heavy chains (MW = 30 000), Gla domain in N-terminal and 2 EGF domains.
Formulation : 50/50 (v/v) glycérol/H₂O
12 000 to 36 000 units/mg
MW(Da) : 50 000
Extinction coef. : 13.9
Advantages
The vast majority of enzymes is pure (without additives) with > 95% purity SDS-PAGE. Expiration date of one year from delivery. Delivery in large quantities. Discount according to quantities.
Informations
An enzyme is a protein that catalyzes a biochemical reaction. It converts a substrate into a product. Each enzyme has a structure adapted to its function and its activity is dependent on an optimum temperature and pH. Factor VII (FVII) is a glycoprotein synthesized by the liver, vitamin k dependent. When tissue factor (TF) appears on the surface of damaged, abnormal or activated vascular endothelium, FVIIa associates with it, initiating the extrinsic pathway of coagulation. The FT-FVIIa complex activates the FX in FXa and the FIX in FIXa.
Documentation
Download the product sheetPrice list, safety data sheets and notices are accessible to our registered customers.



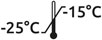


References
| 9-HCVIIA-0031 | Vial | 20 µg |
| 9-HCVIIA-0031-1 | Vial | 1 mg |