HEMOSTASIS COAGULATION RESEARCH REAGENTS ENZYMES ACTIVATED PROTEIN C (APC)
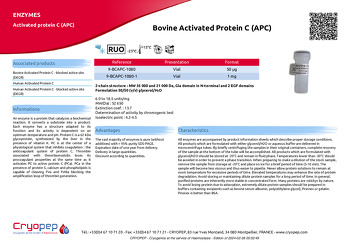
Bovine Activated Protein C (APC)
2-chain structure : MW 35 000 and 21 000 Da, Gla domain in N-terminal and 2 EGF domains
Formulation 50/50 (v/v) glycerol/H₂O
6.0 to 18.5 units/mg
MW(Da) : 52 650
Extinction coef. : 13.7
Determination of activity by chromogenic test
Isoelectric point : 4.2-4.5
Advantages
The vast majority of enzymes is pure (without additives) with > 95% purity SDS-PAGE.
Expiration date of one year from delivery.
Delivery in large quantities.
Discount according to quantities.
Informations
An enzyme is a protein that catalyzes a biochemical reaction. It converts a substrate into a product. Each enzyme has a structure adapted to its function and its activity is dependent on an optimum temperature and pH. Protein C is a 62 kDa glycoprotein, synthesized by the liver in the presence of vitamin K. PC is at the center of a physiological system that inhibits coagulation : the anticoagulant system of protein C. Thrombin associated with thrombomodulin loses its procoagulant properties at the same time as it activates PC to active protein C (PCa). PCa in the presence of protein S, calcium and phospholipids is capable of cleaving FVa and FVIIIa blocking the amplification loop of thrombin generation.
Documentation
Download the product sheetPrice list, safety data sheets and notices are accessible to our registered customers.




References
| 9-BCAPC-1080 | Vial | 50 µg |
| 9-BCAPC-1080-1 | Vial | 1 mg |